World Cancer Day: Understanding Cancer
Cancer is the second-leading cause of death worldwide. It is a disease that seriously affects individuals and their families.
Each year, ten million people die from cancer, with many families experiencing loss and sadness…
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a disease which occurs when changes in a group of normal cells within the body lead to uncontrolled, abnormal growth forming a lump called a tumour; this is true of all cancers except leukaemia (cancer of the blood). If left untreated, tumours can grow and spread into the surrounding normal tissue, or to other parts of the body via the bloodstream and lymphatic systems, and can affect the digestive, nervous, and circulatory systems or release hormones that may affect body function
WorldCancerDay.org
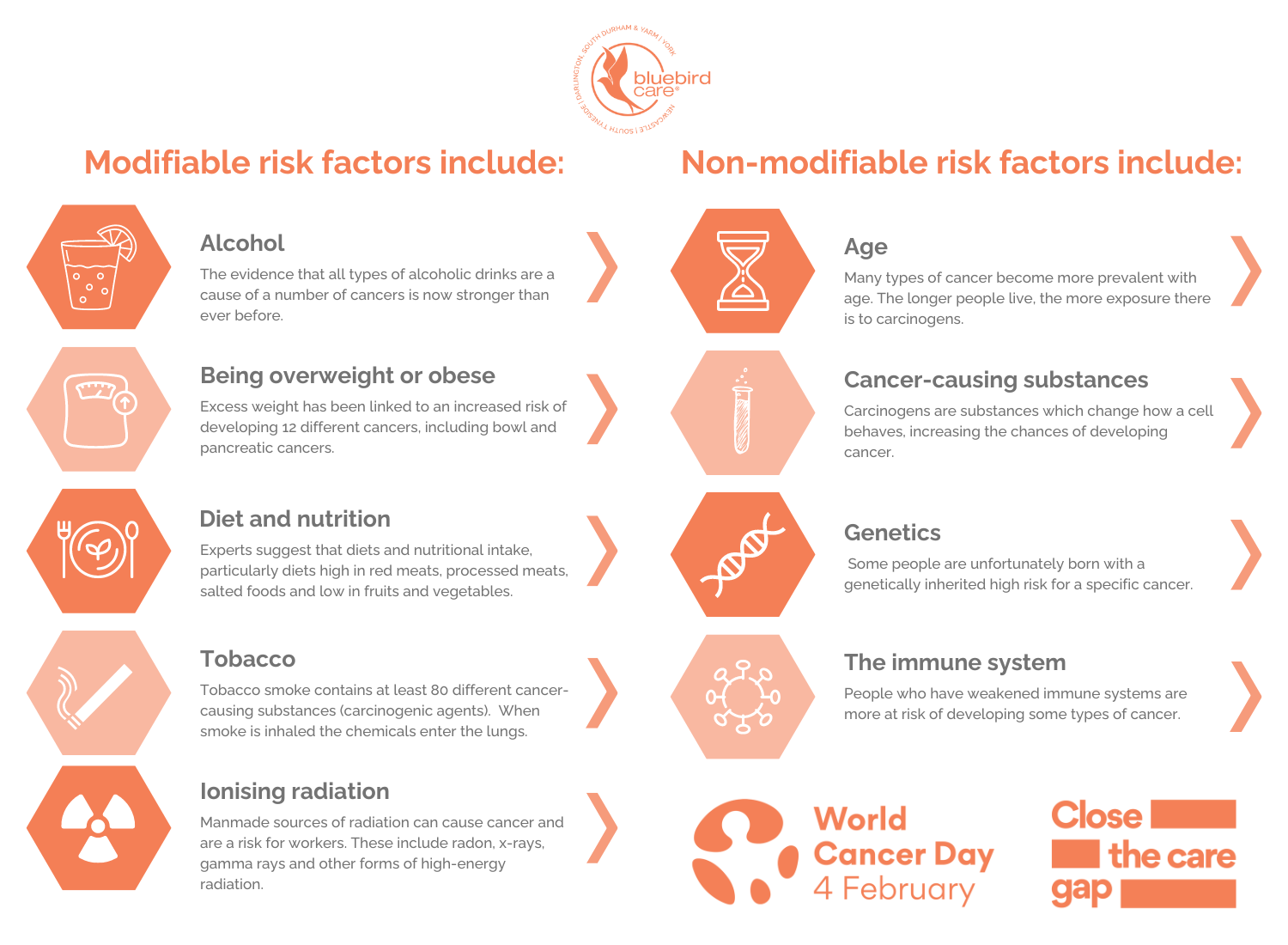
More than 40% of cancer-related deaths are preventable, as they are linked to modifiable risk factors, them being, smoking, alcohol use, poor diet, and physical inactivity. At Bluebird Care, we promote well-being and wellness to both our customers and staff, meaning that we are always promoting keeping a healthy lifestyle to prevent awful diseases, such as Cancer.
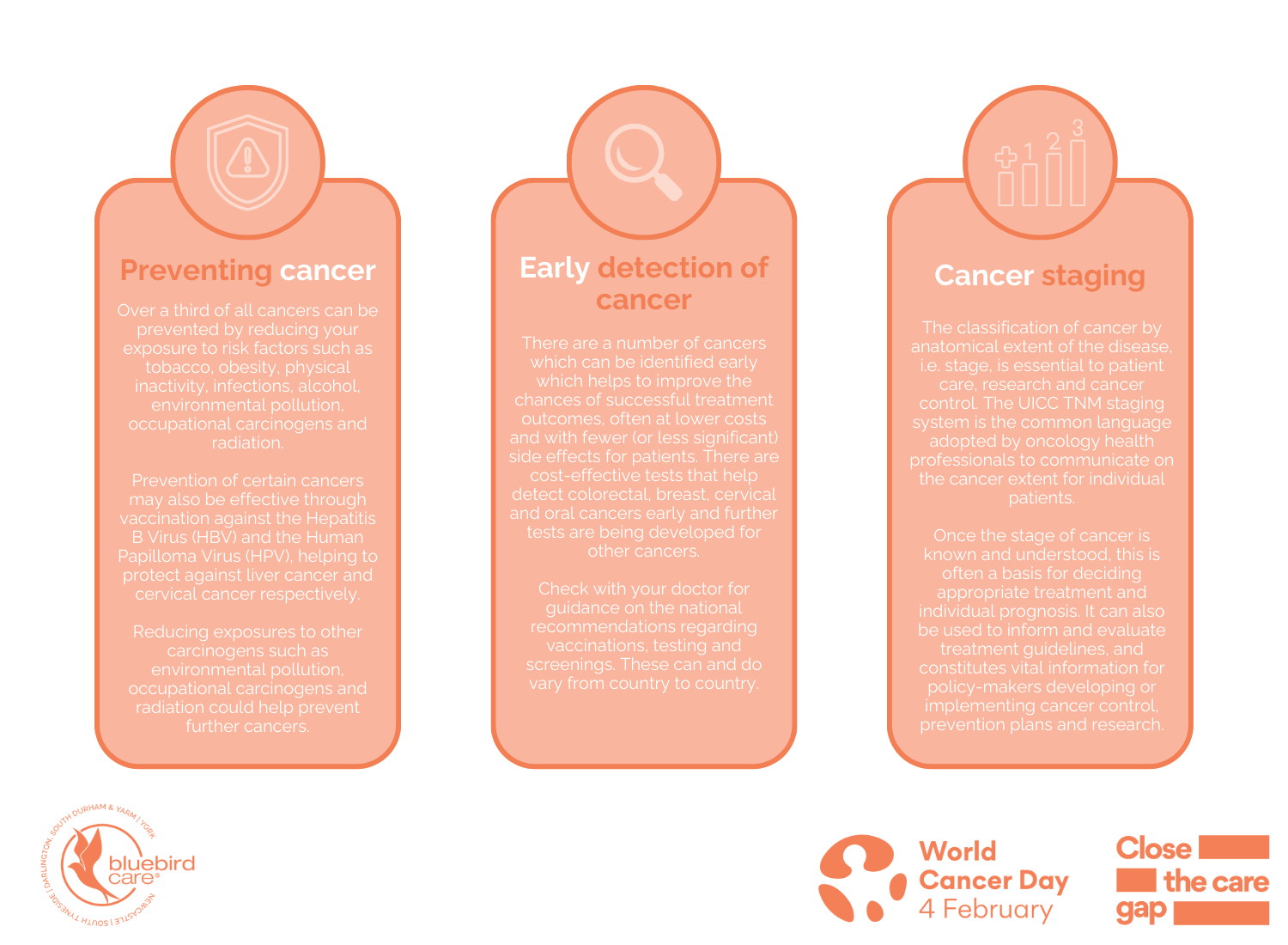
Not only is this disease prevented by promoting a healthy lifestyle, but Millions of lives could be saved each year by implementing resource appropriate strategies for prevention, early detection, and treatment.
Signs and symptoms of cancer
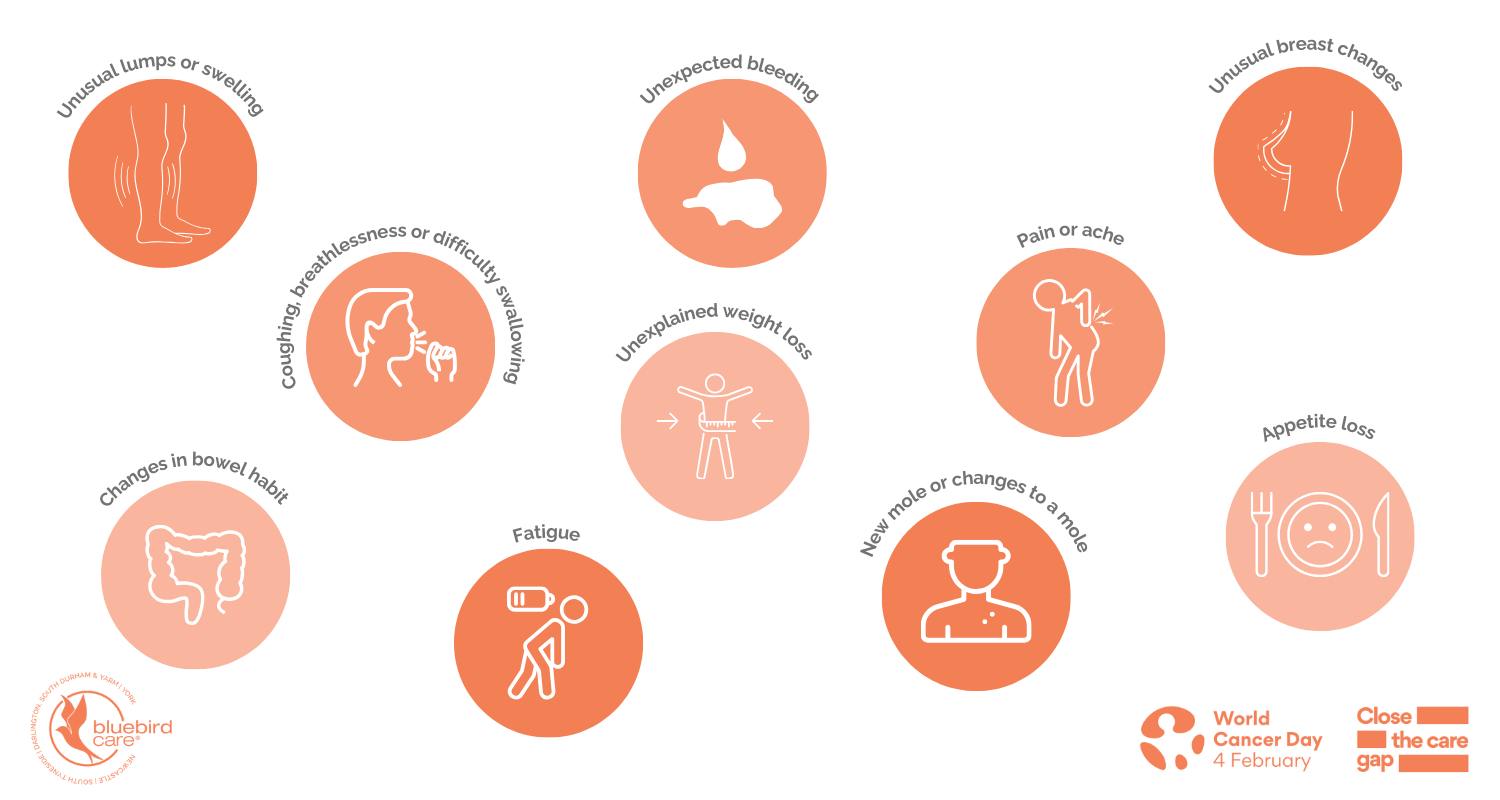
With so many different types of cancers, the symptoms are varied and depend on where the disease is located. However, there are some key signs and symptoms to look out for, including:
- Unusual lumps or swelling – cancerous lumps are often painless and may increase in size as the cancer progresses
- Coughing, breathlessness, or difficulty swallowing – be aware of persistent coughing episodes, breathlessness, or difficulty swallowing
- Changes in bowel habit – such as constipation and diarrhoea and/or blood found in the stools
- Unexpected bleeding – includes bleeding from the vagina, anal passage, or blood found in stools, in urine or when coughing
- Unexplained weight loss – a large amount of unexplained and unintentional weight loss over a short period of time (a couple of months)
- Fatigue – which shows itself as extreme tiredness and a severe lack of energy. If fatigue is due to cancer, individuals normally also have other symptoms
- Pain or ache – includes unexplained or ongoing pain, or pain that comes and goes
- New mole or changes to a mole – look for changes in size, shape, or colour and if it becomes crusty or bleeds or oozes
- Complications with urinating – includes needing to urinate urgently, more frequently, or being unable to go when you need to or experiencing pain while urinating
- Unusual breast changes – look for changes in size, shape or feel, skin changes and pain
- Appetite loss – feeling less hungry than usual for a prolonged period
- A sore or ulcer that will not heal – including a spot, sore wound, or mouth ulcer
- Heartburn or indigestion – persistent or painful heartburn or indigestion
- Heavy night sweats – be aware of very heavy, drenching night sweats
Managing and treating cancer
Your treatment depends on the type of cancer, where your cancer is, how big it is, whether it has spread, and your general health. The general types of treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy, and gene therapy.
Surgery
If a cancer has not metastasised (spread), surgery can remove the entire cancer which may completely cure the disease. Often, this is effective in removing the prostate or a breast or testicle.
Radiotherapy
Radiation treatment or radiotherapy uses high-energy rays to reduce a tumour or destroy cancer cells as a stand-alone treatment and in some cases in combination with other cancer treatments.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses chemicals to interfere with the way cells divide - damaging of DNA - so that cancer cells will destroy themselves. These treatments target any rapidly dividing cells (not necessarily just cancer cells), but normal cells usually can recover from any chemical-induced damage while cancer cells cannot. Chemotherapy is used to treat cancer that has spread or metastasised because the medicines travel throughout the entire body. It is a necessary treatment for some forms of leukaemia and lymphoma.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy uses the body's own immune system to fight the cancer tumour. Immunotherapy may treat the whole body by giving an agent that can shrink tumours.
Hormone therapy
Several cancers have been linked to some types of hormones, including breast and prostate cancer. Hormone therapy works to change hormone production in the body so that cancer cells stop growing or are killed completely.
Gene therapy
The goal of gene therapy is to replace damaged genes with ones that work to address a root cause of cancer: damage to DNA. Other gene-based therapies focus on further damaging cancer cell DNA to the point where the cell destroys themselves. However, gene therapy is new and has not yet resulted in any successful treatments.
The TNM classification focuses on the anatomical extent of the tumour and is determined by assessing the following categories:
- T describes the size of the main (primary) tumour
- N describes whether the cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes
- M describes whether the cancer has metastasised (spread from the primary tumour to another part of the body)
Palliative care
Palliative care runs throughout a patient’s journey from diagnosis to cure or end of life and is designed to relieve symptoms and improve a cancer patient’s quality of life. It can be used to respond to troubling symptoms such as pain or sickness, and to reduce or control the side effects of cancer treatments. In advanced cancer, palliative treatment might help someone to live longer and to live comfortably, even if they cannot be cured.

How to find the right care for you or your relative
1. Find your local office
Bluebird Care delivers care from locally based offices, find yours to start your care journey today.
2. Get in touch with us
Fill in our call back form or give us a call to find out how we can help you.
3. Assessment
We’ll come out to you to find out what you or your loved one needs to help stay independent at home.
4. Care team chosen & care starts
You'll be cared for by our specially trained team to support you to remain at home for as long as possible.

